
Eyelid prolapse
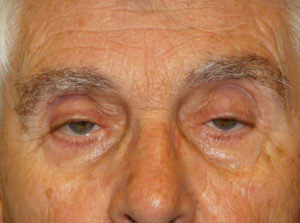
Ptosis is a pathological condition in which one or both eyelids are lower than their correct position, sometimes limiting vision. It can be congenital or acquired. The causes can be many neurological, muscular, post-traumatic, mechanical or even age-related. Depending on the cause and extent of the fall, there are several methods to treat it.
Treatment
This is an operation that is performed under local anesthesia and does not require hospitalization. The incision is made in such a way that it is not visible although the healing of the eyelids is excellent anyway. Excess skin, muscle and fat are removed. Then, depending on the size and type of the problem, the appropriate technique is used to restore the asymmetry of the eyelids. The skin is sutured with very fine sutures. If the eyelid droop concerns only one eye, a standard blepharoplasty needs to be done on the other so that the two eyes are symmetrical.
Recovery
After the operation, the patient can return home because hospitalization is not required. For complete recovery, 10 to 15 days are required until the periocular swellings and hematomas that will be fatally created are absorbed. To limit them, in the first hours after surgery, ice therapy and cold patches are recommended, which together with painkillers reduce post-operative pain. The stitches are removed in 5 to 10 days and for about 1 month heavy physical exercise, swimming and sudden head movements should be avoided.
