
Retinal Vein Occlusion
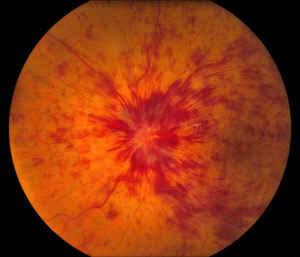
Types of central retinal detachment
- Central vein occlusion (CVA), when the central retinal vein is blocked
- Peripheral vein occlusion (PEO), when one or more smaller peripheral retinal vein branches are blocked
Diseases that increase the risk
- Diabetes
- Hypertension
- Glaucoma
- Atheromatosis/ arteriosclerosis
- Hyperlipidemia
- Blood coagulation disorders
- Complications of a venous occlusion:
- Macular edema
- Eye pain
- Development of pathological neovessels
Treatment
- Intravenous injection of cortisone or anti-VEGF agents
- Laser application
- Vitrectomy surgery
Diagnosis
Diabetic retinopathy is best diagnosed with frequent eye exams by an ophthalmologist, as severe retinopathy can exist without any symptoms.
To find diabetic retinopathy, the doctor observes the inside of the eye using the ophthalmoscope and, if necessary, also performs a fundoscopy
Special paraclinical tests:
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
- Color photography of the bottom
- Fluorography
- Ocular ultrasound
