
Ultrasound
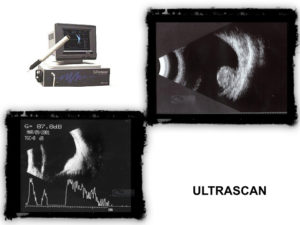
Ocular ultrasound is a special diagnostic ophthalmological examination, based on ultrasound technology (audio waves of a specific frequency), to study the eyeball through a two-dimensional image or through appendages (graphic representations reminiscent of an electrocardiogram).
The sound waves are reflected off the walls of the eyeball and thus we get information about the normal or abnormal anatomy – construction of the fundus and more. Despite the introduction of many new imaging techniques in ophthalmology in recent years, ultrasound remains one of the primary techniques used by ophthalmologists today.
What it is
Ocular ultrasound is a special diagnostic eye examination performed by ophthalmologists that uses ultrasound to study the anatomy of the eyeball through a two-dimensional image of it or through appendages (lines analogous to an electrocardiogram). Ultrasounds are sound waves with a frequency greater than 20,000 Hertz. The frequency we use in ophthalmology is 7.5 to 15 MHz. Ultrasounds are transmitted as waves that reflect on the surface of a medium, in this particular case the layers and walls of the bulb. We receive this ultrasound reflection having information about the anatomy ie. to make the whole bulb normal or not.
When do we do the exam
Ocular ultrasound is usually done when the refractive media are not clear (cornea diseases, dense cataracts, etc.) and we cannot get an image of the fundus of the eye. It is also used with clear media for the differential diagnosis of various diseases or for the measurement of various eye tumors as well as for pathologies concerning the orbit.
For what ailments
- Retina Detachment
- Vitreous hemorrhage
- Choroidal melanoma and other intraocular tumors
- Choroidal detachment
- Bruises
- Intraocular foreign bodies
- Endophthalmitis
- Measurement of striated muscles
- Neoplastic and non-neoplastic pathologies of the orbit.
- Flowing Waterfall
- High myopia
- Congenital glaucoma
